The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), a nonprofit organization with a global reach, is committed to reducing the number of fatalities, injuries, property damage, and monetary losses brought on by fire, electrical problems, and other associated hazards. Established in 1896, the NFPA produces and distributes over 300 rules and standards for home safety and fire prevention worldwide. These regulations cover topics like electrical systems, emergency response, hazardous material handling, and building design guidelines. As a result, the NFPA is essential to advancing safety in businesses and towns. This guide introduces the NFPA, along with the important criteria and the rationale behind its importance.
What Are NFPA Standards?
The National Fire Protection Association’s well-known NFPA guidelines are designed to help lower the chances of electrical failures, fires, and other safety-related problems. These standards offer comprehensive recommendations and best practices for the design, installation, upkeep, and inspection of systems pertaining to emergency response, hazardous materials, building construction, fire safety, and life safety. Governments and other organizations frequently adopt NFPA measures to maintain workplace and site safety, despite the fact that they are not legally binding.
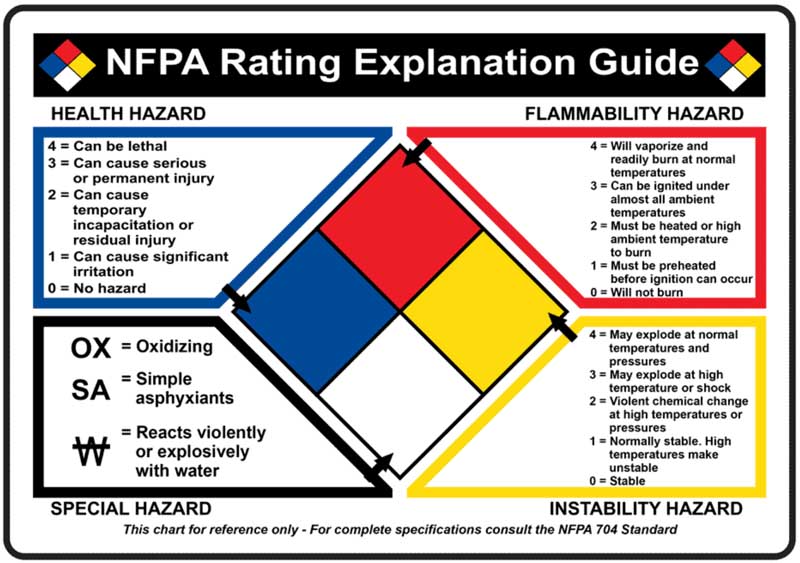
Role and Function of NFPA Standards
1. Development of Fire Safety Codes and Standards
The primary goal of the NFPA is to develop over 300 regulations and standards related to emergency preparedness, electrical safety, fire safety, and construction design. These documents are the result of information from numerous sources that agree on the facts, such as manufacturers, engineers, government representatives, and fire specialists. The regulations are intended to:
- Preserve property and human safety.
- Reduce the possibility of explosions and fires.
- Boost firefighting capabilities
- Encourage adherence to safety protocols and regulations.
Following their establishment, these codes are frequently the basis for both municipal and federal laws and regulations.
2. Training and Professional Certification
To help professionals learn how to correctly apply safety regulations in real-world scenarios, the NFPA provides certification courses and excellent training programs. These initiatives are meant to:
- First responders and firefighters
- Engineers and electricians
- Office managers and building inspectors
- Safety assessors and security personnel
Being certified by the NFPA is a significant accomplishment that helps people grow their careers and enhances safety procedures in public areas and workplaces.
3. Public Education and Awareness
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) works hard to educate the public about fire safety and prevention. The NFPA employs Sparky the Fire Dog as their safety symbol and funds initiatives like Fire Prevention Week to help people prevent fires. They offer:
- Instructional resources for communities and schools that provide advice on fire drills and home safety
- Materials are available in multiple languages to reach a larger audience
Because it teaches families, kids, and individuals at higher risk how to avoid fire hazards and react appropriately in emergency circumstances, this research is significant.
4. Fire Research and Data Analysis
For the NFPA, the Fire Safety Research Foundation conducts a great deal of research. They look into things like what causes fires, how people behave in emergency situations, new technologies, and risk assessment techniques. The NFPA gathers and disseminates a multitude of fire-related data, such as:
The cause of fires
- Notifications of firefighter injuries and deaths
- The trend of house and business fires
- The efficiency of alarms and sprinkler systems
This evidence-based approach enables the NFPA to continuously improve the precision and relevance of its standards by incorporating the most recent data.
5. Technical Support and Code Interpretation
To ensure that the standards are properly understood and used after they are made public, the NFPA also provides professional code translation and expert assistance. They offer:
- Specific news and articles
- Online discussion boards
- Seminars and presentations delivered by professionals
This assistance guarantees that everyone abides by the rules, even under trying or stressful circumstances.
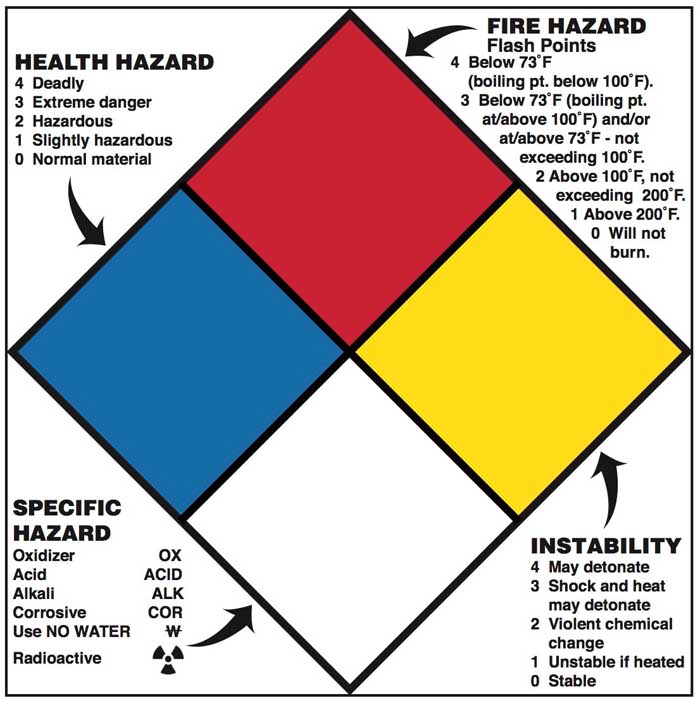
Categories of NFPA Codes and Standards
In order to promote fire safety, save lives, and lower hazards across a range of industries, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) plays a vital and diverse role. By offering and promoting safety regulations and standards, research, training, and education to lessen the global issues brought on by fires and other hazards, its primary goal is to better human life. Below is a list of the NFPA’s primary codes and standards:
1. Fire Protection and Prevention
NFPA 1 – Fire Code
The comprehensive fire safety and prevention manual, NFPA 1, serves as the cornerstone of the entire system. In addition to mentioning more than 130 other NFPA regulations and standards, it covers the fundamental fire safety laws. Understanding this thoroughly is essential since it could serve as the basis for all subsequent scripts.
NFPA 13 – Installation of Sprinkler Systems
Sprinkler system design and installation guidelines are found in NFPA 13. Among the several topics discussed are:
- Sprinkler systems come in various varieties, including wet, dry, preaction, and deluge.
- The best way to distribute sprinklers and where to install them
- Water requires installation methods, materials, and pipe sizes.
In the event of a fire, sprinkler systems that adhere to NFPA 13 are designed to protect persons and property.
NFPA 72 – National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code
It is important to have the right alerts set up so that you, your team, and first responders are all informed in case a fire breaks out. NFPA 72 addresses the location of fires, how to notify or signal others about them, and how to communicate during an emergency. It goes over how to set up and operate manual fire alarm boxes, smoke detectors, and heat detectors. The law also establishes requirements for warning signals that are visible and audible, including their position and volume. There are strict rules governing the fire alarm control devices’ dimensions, use, and efficiency.
2. Electrical Safety
NFPA 70 – National Electrical Code (NEC)
Electrical fires can draw attention to important issues. According to a recent assessment by the U.S. Fire Organization, the number of electrical fires in private structures rose by 6%, and the associated costs rose by 27%. The National Electrical Code, sometimes known as NFPA 70, is crucial in this respect. One of the most widely recognized NFPA standards, this crucial electrical safety regulation is followed across the United States. Every three years, the National Fire Alarm Code, or NFPA 72, is revised to reflect the latest advancements in electrical safety science and technology. It offers comprehensive instructions on safe electrical design, installation techniques, and inspection protocols.
NFPA 70E – Electrical Safety in the Workplace
It offers recommendations for safe work procedures, the need for personal protective equipment (PPE), and workplace risk assessments.
3. Life Safety and Building Codes
NFPA 101 – Life Safety Code
Building safety in an emergency is covered in NFPA 101, which you are likely familiar with if you are familiar with NFPA codes. It offers guidance on:
- Secure exits
- Keeping fires out
- Construction of buildings
This law is a helpful tool for protecting people in a variety of buildings because it applies to both new and older construction. places a high priority on shielding workers from electrical risks like electric shocks and arc flashes.
NFPA 5000 – Building Construction and Safety Code
It is a construction code that covers fire safety, safeguards building inhabitants, and incorporates guidelines for making decisions and breaking conventions.
4. Hazardous Materials
NFPA 30 – Flammable and Combustible Liquids Code
The NFPA 30-Combustible and Combustible Fluids Code establishes guidelines for the handling, storage, and use of flammable liquids in order to lower the risks of contamination, fire, and explosion.
NFPA 400 – Hazardous Materials Code
The storage, use, and handling of a range of hazardous chemicals and materials, such as reactive compounds, gases, and oxidizers, are covered by the NFPA 400—Dangerous Materials Code. These are frequently seen in laboratories, industrial buildings, and fuel storage facilities. This team protects energy systems, machinery, and processes that use heat, fuel, or pressurized equipment.
5. Industrial and Process Safety
NFPA 54 – National Fuel Gas Code
Guidelines for the construction of gas handling systems, devices, and associated components are provided by the National Fuel Gas Code, or NFPA 54.
NFPA 85 – Boiler and Combustion Systems Hazards Code
The NFPA 85 standard is a set of guidelines that address boiler system design, installation, and maintenance and is widely used in homes, businesses, and factories. Its objective is to reduce the risk of explosions and fires in companies and power plants.
6. Traffic Incident Management
NFPA 1500 – Fire Department Occupational Safety
The Fire Department Safety and Health Program, NFPA 1500, specifies the fundamental safety requirements for fire departments. It covers health, safety equipment, training protocols, and safety management plans.
NFPA 1582 – Medical Requirements for Firefighters
The processes for evaluating firefighters’ health to determine if they are psychologically and physically prepared for their line of work are outlined in NFPA 1582, Standard on Health Requirements for Firefighters.
NFPA 1091 – Standard for Traffic Incident Management Personnel Professional Qualifications
The competences needed for incident responders are outlined in NFPA 1091, which guarantees that they are equipped to manage traffic emergencies in a safe and efficient manner.
Why NFPA Standards Matter
- Ensure that safety protocols are uniform across the industry and jurisdiction.
- Reduce the likelihood of electrical, fire, and toxic material incidents
- Make reliable suggestions for the layout and setup of safety measures.
- Assist organizations in meeting their insurance and legal requirements.
- Boost the effectiveness of emergency response and preparation
- Firefighters and other emergency responders are protected by health and safety regulations.
- Support initiatives that increase public awareness and provide safety education.
- Boost the overall resilience of communities, infrastructure, and buildings
Conclusion
In order to promote the safety of buildings, electrical systems, and equipment globally, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) is essential. The NFPA employs stringent guidelines and standards to help safeguard people, property, and the environment against fire and other threats. The fundamental NFPA regulations must be understood and followed by anybody working as a first responder, electrician, office manager, or building inspector. This is about protecting everyone, not just about following the rules.
Time to Ensure NFPA-Aligned Safety products with Jackwin. A well-known manufacturer and supplier of traffic safety equipment in China, Jackwin is dedicated to advancing safer roadways, workplaces, and emergency response environments. Traffic cones, trench coverings, safety signs, parking solutions, and barricade strobe lights are just a few of the many road safety products we provide. All of these are made to comply with international safety standards, to deal with emergency management and accident control requirements.


-80x69.png)

