Возможно, вы уже знаете, что дороги не состоят из одного цельного куска. На самом деле, они встроены в слои дорожного покрытия, чтобы оставаться прочными и служить дольше.
Сегодня вы узнаете, что такое дорожное покрытие и каковы его восемь основных слоёв. Мы также расскажем вам о материалах, которые можно использовать в каждом слое дорожного покрытия.
Что такое тротуар?
Дорожное покрытие — это верхний твёрдый слой дороги. Этот слой прочный и гладкий, что обеспечивает комфортную езду. Он также защищает дорогу от дождя, солнца и других повреждений. Без покрытия дорога может потрескаться или превратиться в грязь.
Вот почему дорожное покрытие — важная часть дорожного строительства. Более того, оно продлевает срок службы дороги. Чтобы по ней можно было ходить, ездить или ездить на велосипеде из одного места в другое.

Типы дорожных покрытий
Дорожное покрытие бывает трёх основных типов. Каждый из них изготавливается по-своему и обладает уникальными свойствами. Ниже представлены категории дорожных покрытий.
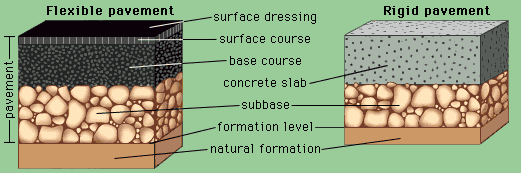
Гибкие слои дорожного покрытия
Гибкие покрытия — это дороги, которые слегка изгибаются при движении транспорта. Как правило, они не обладают высокой прочностью на изгиб, но всё же способны выдерживать интенсивную транспортную нагрузку. Для этого они распределяют давление по разным слоям.
В верхнем слое гибкого дорожного покрытия следует использовать прочный материал по всей площади нижних слоев; можно добавлять и слабые материалы.
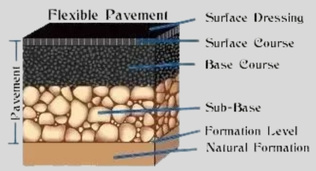
Жесткие слои дорожного покрытия
Жёсткое покрытие выполнено преимущественно из бетона. Верхний слой представляет собой толстую бетонную плиту. Эта конструкция способна выдерживать всю транспортную нагрузку.
Под ним находится базовый слой, состоящий из прочного щебня. Обычно жёсткие слои дорожного покрытия не так сильно гнутся, как гибкие. Они способны сохранять устойчивость даже под воздействием тяжёлых грузовиков.
Композитное дорожное покрытие
Композитное покрытие можно распознать, когда два разных типа дорожного покрытия используются одновременно. Этот слой обладает свойствами как жёсткого, так и гибкого дорожного покрытия. В результате вы получите дорогу с повышенной прочностью и гладкой поверхностью. Этот метод следует выбирать, если вам нужны прочные и простые в ремонте дороги.
8 слоев дорожного покрытия
Чтобы сделать дороги прочными и долговечными, инженеры строят дороги с многослойным покрытием. Все эти слои укладываются друг на друга ступенчато.
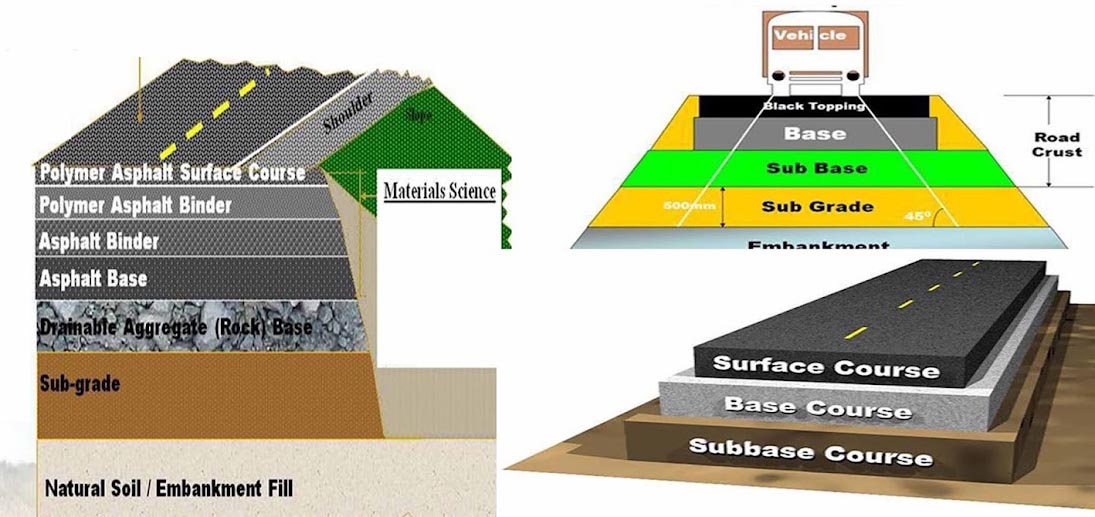
1. Уплотненное земляное полотно
Уплотнённое земляное полотно — это нижний слой дороги. Он состоит из плотно утрамбованного грунта. Этот слой служит основанием дороги, поскольку удерживает все верхние слои.
Поэтому при укладке уплотнённого слоя земляного полотна дорога может легко разрушиться. Его необходимо сделать прочным и ровным, чтобы обеспечить надёжную опору для дороги.
2. Подстилающий слой
Этот слой дорожного покрытия укладывается поверх уплотнённого земляного полотна. Для его изготовления следует использовать прочные материалы, такие как щебень, обожжённый клинкер и гравий. Он выдерживает вес легковых и грузовых автомобилей.
По сути, он служит барьером, препятствующим проникновению воды между верхним и нижним слоями. Благодаря этому дорога всегда будет сухой и прочной. Таким образом, он обеспечивает дополнительную поддержку всех верхних слоёв.
3. Базовый курс
Подложка прочнее подстилающего слоя. Она также сделана из щебня, но способна выдерживать интенсивную нагрузку/вес.
Фактически, он распределяет большую нагрузку от ваших автомобилей и грузовиков на нижние слои. Это помогает предотвратить появление трещин и поддерживать ровность дорожного покрытия.
4. Грунтовочный слой
Грунтовка представляет собой тонкий слой специального масла или жидкости. Её можно распылить на дорогу перед укладкой асфальта. Для этого следует использовать такие материалы, как разжиженный битум или битум, смешанный с водой.
Он создаёт основу для следующего слоя дорожного покрытия, обеспечивая его лучшее сцепление. Конечно, это небольшой слой, но он очень важен для ровной дороги.
5. Связующее покрытие
Нижний слой покрытия представляет собой смесь щебня с очень густой чёрной смолой. Его основная функция — удерживать верхнюю часть дороги на месте. Благодаря этому слою дороги служат дольше и не подвержены растрескиванию. Кроме того, связующий слой также способствует надёжной фиксации верхнего слоя.
6. Подкладочный слой
В дорожном строительстве подгрунтовка представляет собой тонкий слой дорожного покрытия. Этот слой всегда следует укладывать перед укладкой нового слоя асфальта. Он действует как клей между слоями. Без него верхний слой дорожного покрытия может сползти или сместиться. Он обеспечивает устойчивость и помогает дороге оставаться прочной при движении.
7. Поверхностный курс
Верхний слой — это та часть дорожного покрытия, которую вы обычно видите и по которой ездите каждый день. Он сделан из смеси мелкого щебня и битума. Это гладкий, прочный слой, рассчитанный на долгий срок службы.
Верхний слой дорожного покрытия выдерживает большую часть трафика. Более того, он защищает нижние слои от воздействия тепла и дождя. Он также способствует отводу воды с дороги, не позволяя ей скапливаться в лужах.
8. Герметизирующий слой
Наконец, финишное покрытие — это последний слой, наносимый поверх дорожного покрытия. Это тонкий слой жидкого битума и асфальта. Иногда можно добавить и небольшие камни.
Это также поможет предотвратить расширение мелких трещин на дорогах. После нанесения герметика дорога станет гладкой и блестящей.
Дорожные слои и материалы
Каждый слой дорожного покрытия изготавливается из специальных материалов. Например, нижние слои (земляное полотно и подстилающий слой) состоят из грунта, гравия и щебня. Они обеспечивают несущую способность и служат опорой для других участков дороги.
Далее, в базовом и связующем слоях используются более прочные щебни, которые можно смешивать с битумом. Они выдерживают большие нагрузки и продлевают срок службы дороги.
Выше располагается поверхностный и герметизирующий слои, состоящие из мелкого щебня и жидкого битума. Его основная функция — поддерживать ровность дорожного покрытия и защищать его от внешних повреждений.
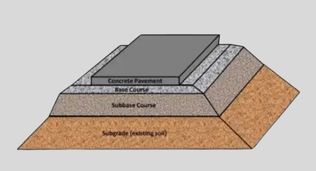
Слои жесткого дорожного покрытия
- Бетонная плита: Это верхний и самый прочный слой жёсткого дорожного покрытия. Для его изготовления используется толстый слой бетона. Однако он не гнётся, как асфальт.
- Базовый курс: Базовый слой добавляется для обеспечения дополнительной поддержки бетона. В качестве материала обычно используется щебень и гравий. Для поддержания нагрузки он распределяет вес с нижними слоями.
- Подоснова: Для создания подстилающего слоя инженеры используют смешанные растворы щебня и песка. Их основная роль — защита фундамента от воздействия воды и предотвращение образования трещин.
- Земляное полотно: Этот нижний слой жёсткого дорожного покрытия содержит уплотнённый естественный грунт. Если слой основания слабый, вся дорога может быть повреждена. Поэтому необходимо убедиться, что он прочный и ровный.
Слои дорожного покрытия: преимущества и недостатки
Ниже приведены некоторые преимущества слоев дорожного покрытия.
- Если ваши дороги имеют прочное дорожное покрытие, их сложнее повредить, и они служат дольше.
- Дороги способны выдержать большие, тяжелые транспортные средства, такие как грузовики и автобусы.
- Защищает дорожное покрытие от трещин и ям.
- Слои дорожного покрытия способствуют равномерному распределению нагрузки, благодаря чему дорога не проседает (не опускается ниже).
- Если вы заметили, что один слой дорожного покрытия сломался, вы можете отремонтировать его, не ремонтируя всю дорогу.
У слоев дорожного покрытия есть и некоторые отрицательные моменты, такие как:
- Если фундамент слабый, то вся дорога может быть повреждена (даже если верхняя часть выглядит нормально).
- Вам придется потратить больше денег, чтобы использовать прочные материалы и правильно построить каждый слой.
- Вы заметите, что в некоторых местах почва может оказаться недостаточно прочной, чтобы удержать все слои вашей дороги.
- Когда вам потребуется отремонтировать самый глубокий слой, вам придется нелегко, поскольку это под силу только большим машинам и высокопрофессиональным рабочим.
Подводя итоги
Подводя итог, можно сказать, что для строительства прочных дорог необходимо грамотное проектирование, использование прочных слоёв дорожного покрытия и тщательное планирование. Вы увидите, как конструкция слоёв дорожного покрытия делает вашу дорогу безопасной для вождения. Если у вас есть вопросы, свяжитесь с нами сегодня, чтобы получить экспертные решения в области дорожной безопасности и строительства.


-80x69.png)

