Workers at construction sites are surrounded by heavy machinery, electrical tools, hazardous chemicals, and moving vehicles, so the danger factor is always there. While in 2024, OSHA saw a 20% drop in fatal falls and a 70% decline in trench-collapse deaths, the construction industry still recorded over 1,000 fatalities and thousands of non-fatal injuries.
Whether you’re a construction site manager, project supervisor, safety officer, or crew member, this guide is prepared for you. Here, you’ll learn about the top 18 hazards in construction sites, based on OSHA data. You’ll also learn the best safety practices to protect your team and maintain a safer, more efficient work environment.
Top 18 Construction Safety Hazards List
Before we start discussing the construction hazards, it’s important to know the root cause. In most cases, construction facilities invest heavily in guarding against machinery-related accidents but overlook the simple hazards that they are actually aware of.
Now take this case shared on Reddit: A carpenter went up to the roof, and he just took two steps, slipped, fell backward, and ended up with a concussion. Why? Because the facility didn’t carry out Pre-Task Planning (PTP), the worker was never infrared about the slippery surface.
That’s exactly why we’re breaking down each most common or let’s say often overlooked hazards at construction sites. So you don’t just get aware of common potential risks, but also know exactly how to respond to it or prevent it altogether.
The most common construction site hazards are:
-
Falls and Slips
Since the construction sites are often uneven, materials and tools are spread in surroundings, so falls and slips incidents in the construction industry happen widely. That’s why it’s the most common OSHA construction hazards.
Falls usually occur when workers lose their balance from heights. Such as falling from ladders, roofs, scaffolding, or open platforms. And the underlying reason is mostly either that the guardrails are not placed, unstable ladders are used, or workers work without wearing safety tools.
Slips, on the other hand, often happen when the ground is wet, muddy, or uneven surfaces. At construction sites, often liquids, morning dew, ice, or scattered debris is always there which can easily cause someone to lose their footing and get injured.
Even though these may seem like basic issues, BLS shared a report stating 38.5% of all construction-worker deaths in 2023, totaling 423 fatalities due to slips, trips and falls, which is almost half of all such fatalities across all U.S. industries.
That’s why it’s important for the construction site managers and supervisors to keep the area clean and ensure that workers must wear safety tools. It is also an equal responsibility towards workers to report about potential fall or slip risks to the concerned department in the first place.

How to Prevent Falls in Construction?
Many construction managers, like you, often ask how to avoid slips, trips and falls in construction industry. Here’s how you can:
- Plan the Work Before Starting: Always conduct Pre-Task Planning (PTP) with your site workers to inform them about fall risks ahead of time. While planning, also guide them how they will do the job and what kind of potential risks might be present.
- Train Workers on Fall Hazards: You should provide OSHA fall protection training to all site workers on the hazard recognition, usage of safety equipment, and tools setup. Even make fall prevention part of your daily safety talks.
- Use Fall Protection Systems and Right Tools: Provide site workers right tools. Like guardrails, safety nets, right height of stable ladders and even good grip shoes. For roof work, setup personal fall arrest systems (PFAS) at the site so that workers can wear safety harnesses while working.
- Maintain Clean Work Areas and Label using Signposts: You should also train the workers on how to handle slippery areas. Like for areas slippery with mud should be covered with stones. While areas slippery due to ice should be covered with grit.
-
Noise and Vibrations
Construction sites, especially on highways, are often loud. So working around loud environments for a long period can cause irreversible hearing loss and tinnitus-ringing issues with workers.
According to the ScienceDirect study, covering stats of 2010-2019, shared that workers exposed to work in loud environments in construction (23%) was higher than the average of other industries (20%).
To reduce the construction noise exposure, facilities should provide workers with tools that operate on low-noise. Like low-noise generators and rotary screw compressors. You should also schedule timings to rotate workers’ shifts to limit their time in high-noise zones. Also, provide them properly fitted earmuffs or earplugs and train your employees on consistent use.

-
Asbestos in Construction Sites
Asbestos is basically a tiny fiber which was widely used in the past until the 1970s for roofing, insulation, and cement-making purposes. According to OSHA collected data, nearly 1.3 million U.S. workers are at risk of asbestos exposure each year.
But now the usage of asbestos material has significantly reduced in the USA due to health concerns. However, several old buildings and homes still contain asbestos-containing materials.
So during construction or renovation, when this material gets damaged, it releases these tiny fibers in air. And once your workers will inhale these fibers, they can pose several fatal and severe diseases like lung scarring, lung cancer, and mesothelioma.
To protect workers from the impact of asbestos, you should primarily educate your workers about asbestos and OSHA standards. Like what it is, how to identify this material and what to do when they come across this material. You should also provide workers with respirators rated for asbestos and protective suits.

-
Danger of Silica Dust Exposure in Construction
Silica is the biggest danger for construction workers after asbestos. According to OSHA and NIOSH, around 2.3 million U.S. workers are exposed to silica dust. Since these deadly particles are found in stones, rocks, bricks, concrete, and mortar, your workers cannot avoid this directly.
There are ways you can train your workers to protect from silica dust. Primarily, you should follow and educate workers about OSHA silica construction standards. Air monitoring and medical exams should also be conducted regularly for exposed workers.

-
Electrical Hazards in Construction
ESFI has, in 2011-2023 data summary, shared that the construction industry had 855, the highest number of fatalities. And mostly painters, roofers, electricians, construction workers, or carpenters are the ones who mostly face electrical fatalities. The electrical injury primarily arises from live wires, faulty equipment, exposed circuits, and even temporary power sources.
To keep workers safe, it’s important to identify utility lines before operating the equipment. Also educate your entire staff, not just electricians on identifying electrical hazards and safe work practices. You should also make it mandatory for all workers to wear OSHA’s recommended Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) at the worksite.

-
Working At Height
Working at height is one of the most deadly jobs and cause of falls from height construction. According to a CDC report, each year 300-400 construction workers die in falls, typically when working on roofs, scaffolds, or ladders.
And to prevent your workers from such hazards, you must train your crew on working at elevated levels. Like how to do the job at heightened levels, use ladders safely, inspect scaffolding before climbing, and wearing PFAS.
In addition to training, It’s also equally important for you to provide the team with right heighten and secure tools, install guardrails and safety net where possible. And restrict them from working at height during bad weather.

-
Airborne Fibres and Materials
Obviously, construction sites have a lot of dust particles in the air, including the airborne fibres. Airborne fibres are the tiny yet dangerous dust particles. When inhaled, they can quietly damage your worker’s lungs and cause chronic obstructive pulmonary disease over time.
Generally, these fibres come from cutting drywall, breaking a concrete object, or demolishing ceiling tiles. So to reduce the inhaling risk, certainly your workers should wear N95 respirators masks. You should also educate your laborers on utilizing wet cutting methods and using ventilation systems at the site.

-
HAVS Hand Arm Vibration Syndrome
Hand arm vibration syndrome, also known as Vibration white finger (VWF), is a serious and painful condition which occurs due to using vibrating hand tools for long-term. This condition doesn’t appear at once. Your workers may experience this over time.
In early signs, they may experience blanching (turning white), numbness, pain in the fingers, or even loss of grip strength. If ignored, it can cause permanent damage to your workers.
Fortunately, this risk is preventable. Site managers like you, must monitor tool vibration levels and schedule tasks between workers in a way that no one performs the job for longer. You should also provide the laborers with low-vibration tools and ensure that they must wear anti-vibration gloves.
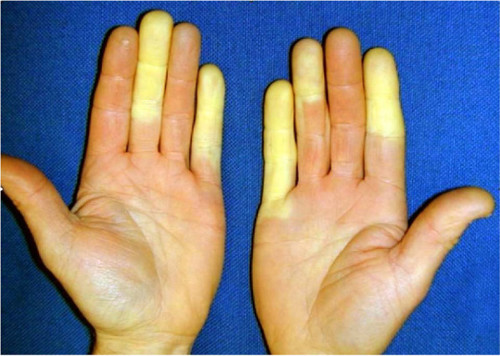
-
Moving Objects
Hazard of struck-by object construction is one of the common construction accidents and workers’ deaths. As per the OSHA, 75% or one-in-four heavy machinery accidents construction sites occur due to struck by vehicle and heavy equipment. Such as trucks, forklifts, swinging loads, constructing masonry walls or rolling equipment.
You may ask how to avoid struck-by hazards? As per OSHA guidelines:
- When doing construction along or on public roads, managers like you should set up proper traffic signs and barricades. This will help you create a safe boundary for your workers.
- Before each shift, you should inspect the vehicle or hire a person for vehicle inspection to ensure that all parts are in working condition.
- While loading material, all staff and laborers should be in a clear area to avoid the struck-by risk.
- Drivers should park the vehicles on a leveled surface. In inclined surfaces, they should park using chocks.
- You should also ensure that all your facility staff including workers and laborers must be wearing a high-visibility orange/red vests.

-
Collapsing Trenches
Trench collapses (often known as trench cave-in) is the situation when a wall of a trench falls in, burying workers. This is one of the most deadly hazards in construction sites as just one cubic yard of soil weighs almost equal to a car weight.
To prevent trench collapses, site managers like you, must follow OSHA trenching and excavation standards. After rain, vibrations, or load shifts, you should also first inspect the trench and then workers perform tasks.
Also, any heavy equipment and spoil piles (excavated soil) should be placed at least 2 feet away from the trench edge to avoid their impact with the trench wall. You should also provide laborers with safe and stable ladders.

-
Hazardous Materials
Several hazardous and chemical materials are present in construction sites. Most common include silica, asbestos, gasoline, solvents, diesel fuel, and adhesives. If they are not handled properly or kept opened for longer, they can mix in the air and pose severe health issues to your workers. Such as skin irritation, or even long-term illnesses (cancer or organ damage).
To protect your workers from construction chemical exposure, you must adhere to OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard (HCS). You should also ensure that all the materials are properly labeled and kept at safe place. You must also provide laborers safety tools and train them on how to safely handle, store, and dispose of these substances.

-
Material and Manual Handling
Your construction workers may constantly move and shift material around the site. Whether they shift manually or use lifting equipment, handling risk is always there. Even in most times, upon constantly shifting material from an inclined surface, construction fatigue hazards can occur in the form of:
- Back injuries
- Muscle strains
- Slips or falls
- Dropped loads causing crush injuries
As per BLS report, in 2020, the incidence rate of overexertion and bodily reaction for construction laborers was 48.3 cases per 10,000 full-time workers.
However, there are ways to reduce this hazard. You should as a site manager train workers on proper lifting techniques (e.g., lift with the legs, not the back). Instruct them about using mechanical aids like forklifts, hoists, or dollies whenever possible. In addition, you should also educate workers about OSHA materials handling and storage guidelines.

-
Scaffolding Safety Hazards
While Scaffold is a great help during long-building’s construction, it can pose severe safety risks for your workers, if not used properly. Mostly, this hazard arises when guardrails are not setup or due to overloading of equipments and workers, leading to falls and even structural collapse during construction
To ensure safety, you must ensure that the scaffold is structured by following OSHA guidelines. You should also ensure that scaffold is equipped with proper guardrails and toe boards, and never overloaded. Your workers should also have safe access and receive training on how to use scaffolding systems correctly.

-
Confined Space Construction Hazards
While working in confined spaces, limited airflow, toxic gases, or low oxygen, are the most deadly hazards. Even poisonous gases, liquids, and dust build up can anytime turn to a life-threatening situation for your worker.
To avoid these hazards, as per OSHA guidelines for confined spaces, employers like you must identify and label confined spaces. You should also test the air inside the space and provide a proper ventilation system to the laborers. You should also ensure that workers never enter without training, and always wear the right protective gear.

-
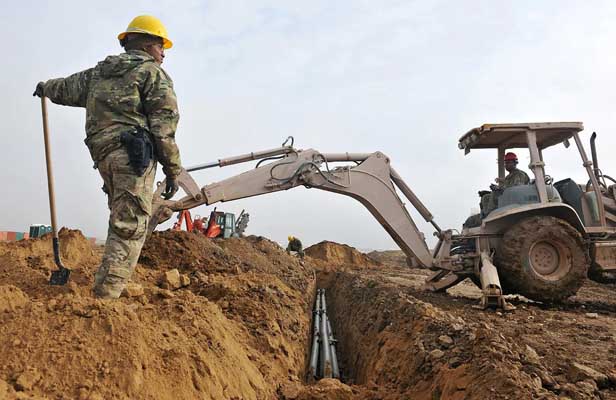
Excavations
Fatalities or injuries often occur while doing excavation trench collapse or laying foundations. To avoid this hazard, OSHA has designed and mandated certain excavation regulations which you should follow and educate your workers.
You should also ensure that the heavy equipment and excavated material is placed at least 2 feet away from trench edges. Also, instruct your workers to not enter a trench unless all safety measures are in place.

-
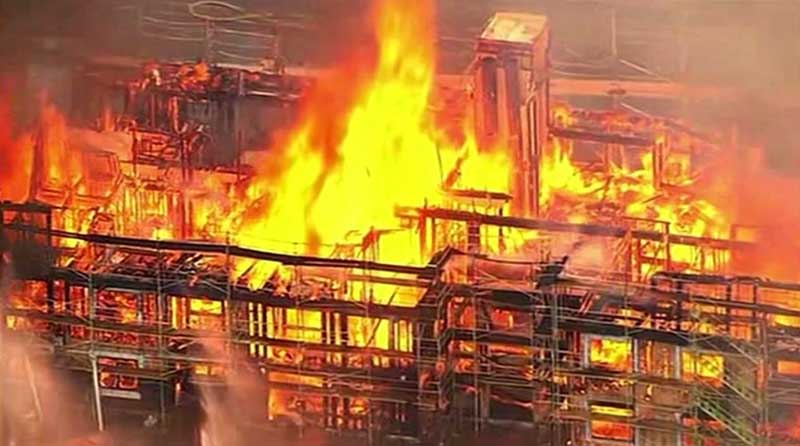
Construction Site Fire Risks
Construction sites have a higher risk of fires because of several flammable materials like wood, insulation, paint, and fuel stored onsite. While construction, your workers may also do the welding or cutting and a single spark can quickly turn into a fire. Even faulty electrical wiring, glass and poor housekeeping add to the risk.
To avoid fire hazards, site managers must follow fire safety protocols. Like you should keep flammable items away from ignition sources and store materials properly. You should also provide fire extinguishers at key locations and train your workers on what to do in case of a fire.

-
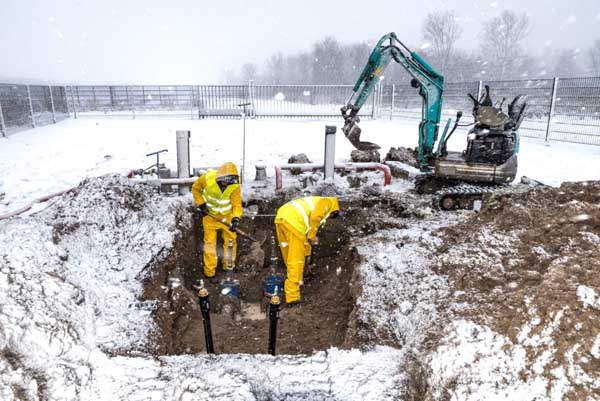
Weather Hazards Construction
In different weather conditions, working in the outdoors, even during daytime or nighttime, can sometimes become dangerous for your site workers. Now imagine that your team is working during the daytime under the direct sun. Within an hour, workers may start feeling dizzy or even collapse without proper hydration, break, or heatstroke.
Even during working at nighttime, due to poor visibility, workers might slip on wet surfaces. In addition, situations in windy or rainy weather can become more dangerous. To protect your workers, facilities should monitor weather conditions regularly and schedule work accordingly. You should also provide workers cooling vests in summer or thermal clothing in winter.

-
Ergonomic Hazards in Construction
Ergonomics hazards typically occur when workers continuously perform the same task. Like they repeatedly lift heavy materials, use awkward postures, bend or twist frequently, or perform long period tasks (such as hammering or drilling).
Over time, these actions can pose muscle strains, lower back pain, tendonitis, and joint damage to your workers. This effect on workers may not just impact their health but also slow down your project progress.
To reduce the risk, site managers should rotate tasks and provide mechanical lifting aids for workers to help. You should even train workers on safe body mechanics and allocate time for their breaks and refreshments.

What are the Fatal Four in Construction OSHA?
As per OSHA, Fatal Four refers to the top four hazards of worker deaths in the U.S. construction industry. These four hazards are:
- Falls: Falls are the leading cause of construction deaths. As workers often work on ladders, roofs, scaffolds, and other elevated surfaces, so falling risk is probably high.
- Struck-By Objects: Construction sites have several tools, vehicles and equipment moving around. So workers are widely hit by these objects and get injured.
- Electrocutions: Electronic hazard means hazard that occurs when workers get in contact with live wires, power lines, faulty wiring, or ungrounded equipment. This often leads to serious or fatal electric shock.
- Caught-In or Caught-Between: At construction sites, during performing tasks, workers often get crushed or trapped between equipment, walls, structures, or even trenches. This is also the wide cause of construction workers fatalities.
OSHA reports that if these Fatal Four hazards are controlled, it would save approximately 500 lives each year in the U.S. construction industry.
Mental Health Construction Industry
In a report, CDC shared that nearly 30% of male construction workers experienced serious mental issues like psychological distress, and 2.5% had even thought about suicide in the previous year. Construction workers are widely facing mental issues.
But how do you deal with the rise of mental issues among workers? Although there are no proven ways, there are few things you can do to handle such a situation wisely.
The most basic thing you can do is build a supportive culture at the workplace and manage workload and hours between labors so no one does long period shifts. It’s also important to launch a campaign about mental health to increase awareness among workers.
Conclusion
The construction site is full of hazards, and in this guide, we’ve explained the top 18 hazards in construction sites and how to avoid them. But these aren’t the only dangers. There are many more that can emerge unexpectedly. That’s why it’s absolutely crucial to take site and worker safety seriously.
JACKWIN, is one of the leading worksites’ safety products manufacturer and supplier since 2008. Whether you need high-visibility clothing, safety barriers, construction cones, or even guardrails, contact us today to get in wholesale prices. Our professional team can also manufacture a customized product for your needs.


-80x69.png)

