The global market of carbon steel was worth USD 1.63 trillion in 2025. According to the latest studies, it will cross USD 1.72 trillion in 2026. The reason is that carbon steel is widely used in manufacturing, medical, automobile, and construction industries.
But there are several types of carbon steel, and you should know which one is most suitable for your project. Let’s find out in this simple guide!

Carbon Steel Composition
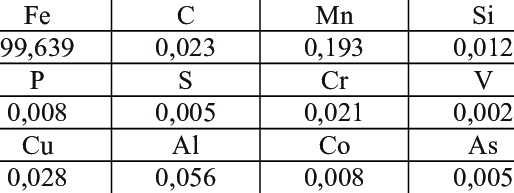
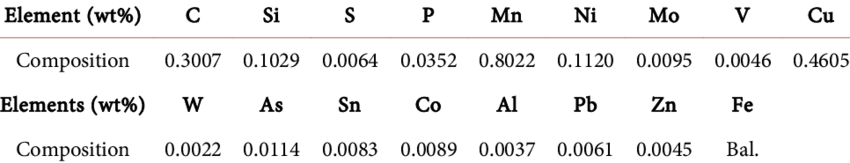
Carbon steel is mainly made of iron and carbon. These two elements decide the strength and hardness of steel.
-
- Iron (Fe): 98-99% of the alloy
- Carbon (C): 0.05% to 2.0%
- Manganese (Mn): 0.3% – 1.0%
- Silicon (Si): Used to remove oxygen during steelmaking.
- Sulfur (S) & Phosphorus (P): These are impurities.
Types of Carbon Steel Based on Carbon Content
The carbon content changes the overall strength and flexibility of carbon steel. On the basis of carbon levels, you can classify carbon steel into the following main types.
1. Low Carbon Steel (Mild Steel)
Low carbon steel has a small amount of carbon, approx. 0.05% to 0.32%. Due to this composition, you can mold it into any shape you want. However, it is not very strong but is flexible and easy to work with.
You can cut or weld it without much effort. Mild steel is also less expensive as compared to other types of carbon steel. You can use it for pipes, car bodies, building parts and in machinery manufacturing.
Low Carbon Steel Properties: Soft, good ductility and weldability. It can rust without coating.
Types of Low Carbon Steel: Low carbon steel has a few main types based on its strength and applications.
| Low Carbon Steel Type | Industry | Uses |
| Low Carbon Structural Steel | Construction | Bridges, columns, building & structural framing |
| Low Carbon Strip Steel | Sheet Metal Work | Automobile parts, metal stamping, construction tools and binding materials |
| Low Carbon Galvanized Steel | HVAC, automotive, construction | Roofing, automotive parts, road barriers, traffic sign poles and HVAC systems |
| Low Carbon Tubing Steel | Construction, heavy equipment, automotive, oil & gas | Machine tubes, fluid pipes, plus support tubing |
| Pressure Vessel Steel | Machinery manufacturing, heavy equipment | Storage tanks, oil/gas, chemical, and power generation |
2. Medium Carbon Steel
Medium carbon steel contains 0.30% to 0.60% carbon. It is stronger and harder than low carbon steel but less flexible. Also, this type of steel gives you a good balance between hardness and toughness.
Medium Carbon Steel Properties: Higher strength, moderate ductility, get hard by heat treatment, good wear resistance and less easy for you to weld/shape.
Types of Medium Carbon Steel: Medium carbon steel divided into different types based on its composition and use.
| Grade/Type | Carbon Content (%) | Applications |
| 4140 Steel | 0.38 to 0.43 | Automotive, aerospace, oil or gas and in machinery parts. |
| 1060 Steel | 0.55 – 0.65 | Use in springs, railway wheels, traffic bollards, blades, shafts and automotive parts. |
| 1045 Steel | 0.43 to 0.50 | You can use it in gears, axles, bolts, shafts and machine parts. |
3. High Carbon Steel
The carbon content in high carbon steel is between 0.60% and 1.00%. You will find it very hard and strong but less flexible. If you want to increase its hardness further, you can achieve this by heat treatment. Moreover, high carbon steel is ideal for you when you need a sharp edge or durable parts.
High Carbon Steel Properties:
- Very hard and strong
- Low ductility & flexibility
- Excellent wear resistance
- Can be easily cracked if bent too much
- 485 MPa yield strength
- Tempering capability
- Moderate corrosion resistance
- Heat treatment responsiveness
| Types of High Carbon Steel | Added Elements/Composition | Applications |
| Alloyed Steel | Chromium, cobalt, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, tungsten & vanadium | Stainless steel and high-strength parts |
| Spring Steel | Carbon 0.6 – 1.0% and silicon for flexibility | Use to build springs and flexible parts |
| Plain Carbon Steel | Carbon only, no significant alloying elements | Cheap high-carbon applications, street light poles and for general use |
| Tool Steel | Tungsten, molybdenum plus sometimes other alloys | Cutting tools, dies & high-strength tools |
4. Ultra-High Carbon Steel
Ultra-high carbon steel has roughly 1.00% to 2.00% carbon. It is extremely hard and strong. But, this steel type is not very flexible. It is mostly made of iron and carbon. Sometimes, small amounts of other elements such as manganese or silicon are also added to improve performance. It’s very difficult for you to shape or weld it. That’s why you need to carefully process it with heat treatment and special tools.
Ultra High Carbon Steel Properties:
- Rich in carbon
- Very hard
- Strong tensile strength
- Excellent wear resistance
- Low flexibility / ductility
- Limited corrosion resistance
- Can be heat-treated
Applications: You can use it in cutting tools, dies, molds, springs, rollers, high-strength cables, durable automotive and aerospace parts.
Types of Plain Carbon Steel (Based on Manufacturing Process)
-
Killed Carbon Steel
Killed carbon steel is fully deoxidized during production. For that purpose, aluminum or silicon is added to remove oxygen. This prevents gas bubbles from forming in the steel. These properties make it uniform and free of porosity. Plus, it has a smooth surface. You can use this steel when consistency and strength are important for you.
-
Semi killed Carbon Steel
During its manufacturing, semi-killed carbon steel is partially deoxidized. However, some gas remains in the steel, so it is not as uniform as killed steel. You can make it by adding a smaller amount of deoxidizers such as aluminum or silicon compared to killed steel.
This method makes it affordable to produce while maintaining good strength. Semi-killed steel is ideal for you to use in structural parts, plates, galvanized tire wires and rolled products.
-
Rimmed Steel
Rimmed steel is made by lightly removing oxygen during production. This lets some gases escape slowly. As a result, it makes the steel smooth on the outside but less uniform inside and low in impurities.
You can easily cut, mold plus form this carbon steel. If we talk about its major applications, these include sheet metal, cold-rolled products and parts where a clean surface is important.
Types of Carbon Steel For Knives
- 1095 Carbon Steel is a very popular material for knives. It has about 0.95% carbon. This steel can holds a sharp edge well and is easy for you to sharpen.
- 5160 Carbon Steel often used in large knives or swords manufacturing. It is slightly more flexible and tough.
- 52100 Steel is a high-carbon alloy steel with excellent wear resistance. You can use it for high-end knives.
- O1 Tool Steel type is known for its hardness and edge retention. That’s why it is widely used for cutting tools and knives.
- D2 Steel is a high-carbon and rich-chromium steel. Hence it’s also called semi-stainless. This carbon steel is very wear-resistant and can hold an edge for a long time.
Grades of Carbon Steel
Grades of carbon steel are classifications which show you the strength and carbon content of the steel. Higher grades mostly mean stronger and harder steel, while lower grades are softer and easier to work with.
Carbon Steel Grades Chart
| Grade | Carbon Content (%) | Hardness Level | Common Uses |
| 1018 | 0.15 to 0.20 | Soft and easy to shape | Sheet metal, rods and general fabrication |
| 1045 | 0.43 – 0.50 | Has medium strength and tougher | Shafts, gears, machinery parts |
| 1060 | Approx. 0.55 to 0.66 | Mostly hard and can holds edge better | Widely used in springs, knives & blades |
| 1095 | Constant 0.90 – 1.03 carbon | Very hard and sharp edge | Ideal for high-carbon knives and cutting tools |
| 4140 | 0.38 – 0.43 | It is strong and tough | Used in automotive industry and shafts |
| 5160 | In the range of 0.56 to 0.64 | 5160 steel is flexible but strong | Better for swords, large knives plus springs |
Conclusion
In the end, you now have good information about all carbon steel types and their applications in different sectors. We recommend you to always check the carbon content to make sure the steel matches your project’s purpose.
At JACKWIN factory, we have a large stock of road and traffic safety products which are made with carbon steel. So you can message us to get quotes or expert guidance anytime.
People Also Ask
Carbon Percentage in Stainless Steel
Stainless steel contains 0.03% to 1.2% carbon, but this range depends on the type of stainless steel. You will find lower carbon stainless steel soft and easy to shape. If stainless steel has high carbon, it will be hard and can hold a sharper edge.
Is 4140 Carbon Steel?
4140 steel is a carbon steel but not pure. It also has chromium and molybdenum along with carbon. This type is a medium carbon steel known for its strength and wear resistance.
Does High Carbon Steel Rust?
Yes, high carbon steel can rust because it contains a lot of carbon but little or no chromium. If you want to prevent rust, you need to keep it dry and clean. You should also occasionally oil it, because you can’t make it rust proof.
Is Carbon Steel Safe For Cooking?
Absolutely yes. Because carbon steel is made of iron and carbon, it naturally forms a non-stick surface when seasoned. Unlike some non-stick pans, carbon steel does not contain any harmful chemicals such as PFOA or PFAS.
Why is Carbon Steel Better Than Stainless?
Carbon steel is better as compared to stainless steel, because it is stronger as well as less expensive. And, it can be made into very sharp and durable tools. Carbon steel can also handle higher heat, which makes it great for construction & structural parts.


-80x69.png)

